What’s the diagnosis?
Lifelong irregular pale patches
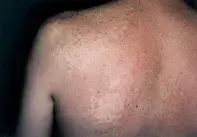
Figure. Multiple irregular hypopigmented patches contrasting with surrounding erythema over the shoulder and back.
Differential Diagnosis
Pityriasis versicolor is an acquired disorder characterised by pale, scaling patches. Skin scrapings will reveal short hyphal elements with groups of spores typical of pityrosporum organisms.
Leprosy is an acquired condition that may present with hypopigmented patches in the indeterminate phase of the infection. Decreased sensation may be demonstrable. Skin biopsy usually reveals neural inflammation and acid-fast bacilli.
Tuberous sclerosis is an autosomal dominantly inherited disorder that may present with multiple pale macules in the shape of ash leaves, preceding the other stigmata. The pale areas are usually present at birth and noted in the neonatal period. UV light examination may accentuate these lesions in pale skin. Biopsy shows decreased melanin in the epidermis due to disturbance in melanin production.
Vitiligo is an acquired disorder associated with irregular white patches often localised in periorificial areas or acrally. Skin biopsy shows loss of melanocytes.
Naevus depigmentosus (achromic naevus) presents in infancy as irregular areas of hypomelanosis. The decreased pigmentation is due to abnormalities in melanocyte transfer to surrounding keratinocytes in the skin.
Piebaldism is associated with irregular white patches, particularly present in the midline and often associated with a white forelock. Skin biopsy shows loss of melanocytes and the white skin is identical to that seen in acquired vitiligo.
Naevus anemicus is the correct diagnosis and represents an unusual abnormality of cutaneous vessels that are associated with increased sensitivity to catecholamines. The lesions may be solitary or multiple. Skin biopsy is unhelpful. Mechanical stimulation of the skin fails to induce a vascular flare. Intralesional injection of antihistamine, nicotine, 5-hydroxytryptamine, bradykinin or acetylcholine fails to induce erythema. Sympathetic blockade or intralesional injections of alpha adregenic blocking agents will induce erythema. Naevus anemicus may be highlighted by a surrounding erythema induced by heat. Persistent erythema can represent surrounding vascular naevi such as naevus flammeus. No treatment is usually necessary.
A 32-year-old man had a lifelong history of a series of asymptomatic, irregular, pale patches concentrated on his left upper shoulder and back. There was no associated scaling, and the surrounding skin had a pink blush. Stroking of the skin failed to elicit dermographism or a flare within the pale patches (Figure). No skin biopsy was obtained.

